The research team led by Prof. Xiao-Ming Li has recently published an article titled Distinct Circuits from Central Lateral Amygdala to Ventral Part of Bed Nucleus of Stria Terminalis Regulate Different Fear Memory in Biological Psychiatry on Sep 5th, Beijing time.
This research established a functional role for distinct central lateral amygdala to ventral part of stria terminalis circuits in the differential regulation and appropriate maintenance of fear.
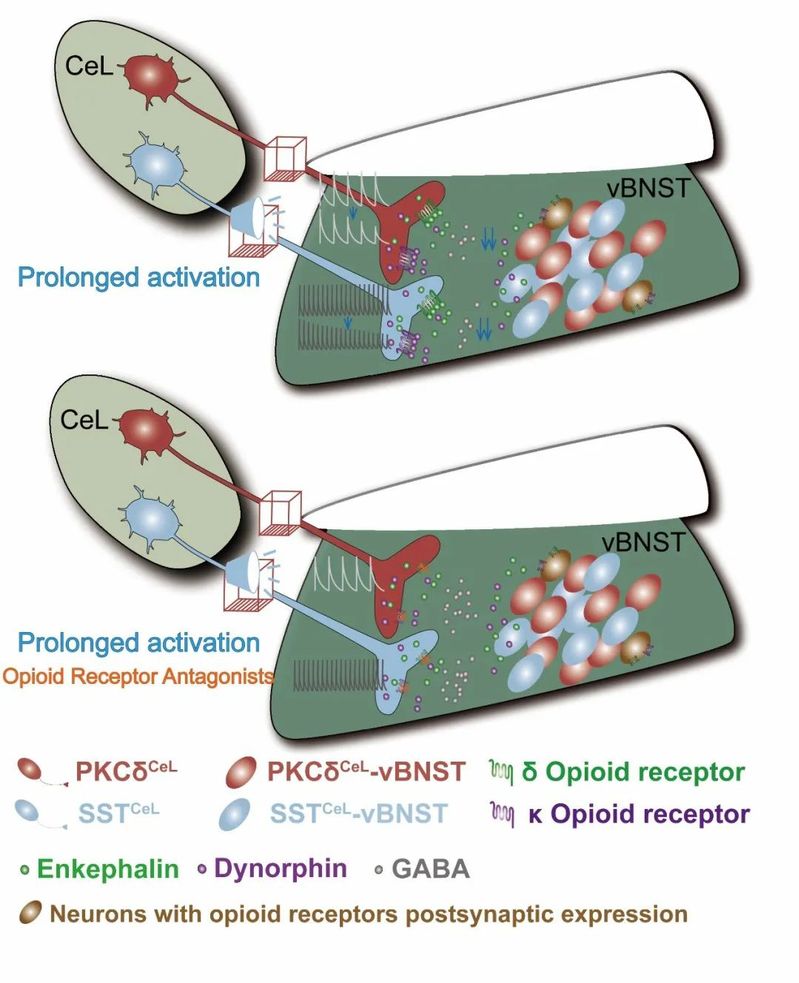
The ability to differentiate stimuli predicting fear is critical for survival, however, the underlying molecular and circuit mechanisms remain poorly understood. This work identified the projections from central lateral amygdala (CeL) protein kinase C δ (PKCδ) positive neurons and somatostatin (SST) positive neurons to the ventral part of bed nucleus of stria terminalis (vBNST) GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons. Prolonged optogenetic activation or inhibition of PKCδCeL-vBNST pathway specifically reduced context fear memory, whereas SSTCeL-vBNST pathway mainly reduced tone fear memory. Intriguingly, optogenetic manipulation of vBNST neurons received the projection from PKCδCeL exerted bidirectional regulation of context fear, whereas manipulation of vBNST neurons received the projection from SSTCeL neurons could bidirectionally regulate both context and tone fear memory. The presence of δ and κ opioid receptor protein expression within the CeL-vBNST circuits potentially accounted for the discrepancy between prolonged activation of GABAergic circuits and inhibition of downstream vBNST neurons. Finally, administration of an opioid receptor antagonist cocktail on the PKCδCeL-vBNST or SSTCeL-vBNST pathway successfully restored context or tone fear memory reduction induced by prolonged activation of the circuits. This study provides the first evidence that distinct extended amygdala circuits participated in differently regulating fear memory, which can pave the way for an innovative approach to drug development for a range of fear-related syndromes.
Pro. Xiao-Ming Li from Zhejiang University School of Medicine is the main corresponding author. Dr Yi Zhu, PhD candidates Shi-Ze Xie and Ai-Bing Peng are the first authors. This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, STI2030-Major Projects, Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province, Key R&D Program of Zhejiang Province, Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences, Innovative and Entrepreneur Team of Zhejiang for 2020 Biomarker-Driven Basic and Translational Research on Major Brain Diseases and the fellowship of China Postdoctoral Science Foundation.




 Location :
Location : 

