Adult neurogenesis is impaired in the hippocampus of patients with Alzheimer disease (AD) as well as AD models. However, it is far from clear how modulating adult neurogenesis affects AD neuropathology. A team led by Dr. Binggui Sun, a principal investigator at Zhejiang University School of Brain Science and Brain Medicine, reported that inhibiting adult neurogenesis improved synaptic and cognitive functions in mouse models of AD. Their new paper entitled “Deleting Adult Neural Stem Cells Improves Synaptic and Cognitive Functions in Alzheimer Models” appeared online in Stem Cell Reports on Dec. 30, 2020.
The authors first applied multiple approaches including DCX staining, labeling with retrovirus-expressing GFP and reporter line of mice to compare adult hippocampal neurogenesis in AD mice. They confirmed that adult hippocampal neurogenesis was impaired in two AD models (APP/PS1 and hAPP-J20). Then they inhibited the adult neurogenesis by ablating adult neural stem cells (aNSCs) via genetic and pharmacological approaches, and their data revealed that cognitive functions were improved in AD models after ablating aNSCs. Ablation of aNSCs did not affect the levels of amyloid β but restored the normal synaptic transmission in the dentate gyrus (DG) granule cells of AD models. Furthermore, calbindin depletion in the DG of AD mice was ameliorated after aNSC ablation, and knocking down calbindin abolished the effects of aNSC ablation on synaptic and cognitive functions of AD mice. Together, their data suggest that cognitive functions of AD mice are improved after aNSC ablation, which is associated with the restoration of synaptic transmission in the DG granule cells with calbindin as an important mediator.
Drs Xiaoqin Zhang, Yufei Mei and Yang He are co-first authors of this paper. Drs Binggui Sun and Yudong Zhou are the corresponding authors. Other participants of this study include Dongpi Wang, Jing Wang, Xiaojie Wei, Enlu Yang, Dongming Zhou, Haowei Shen, Guoping Peng, Qiang Shu, Xuekun Li, and Benyan Luo. This study was supported by grants from National Key Research and Development Program of China, National Natural Science Foundation of China, and Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province.
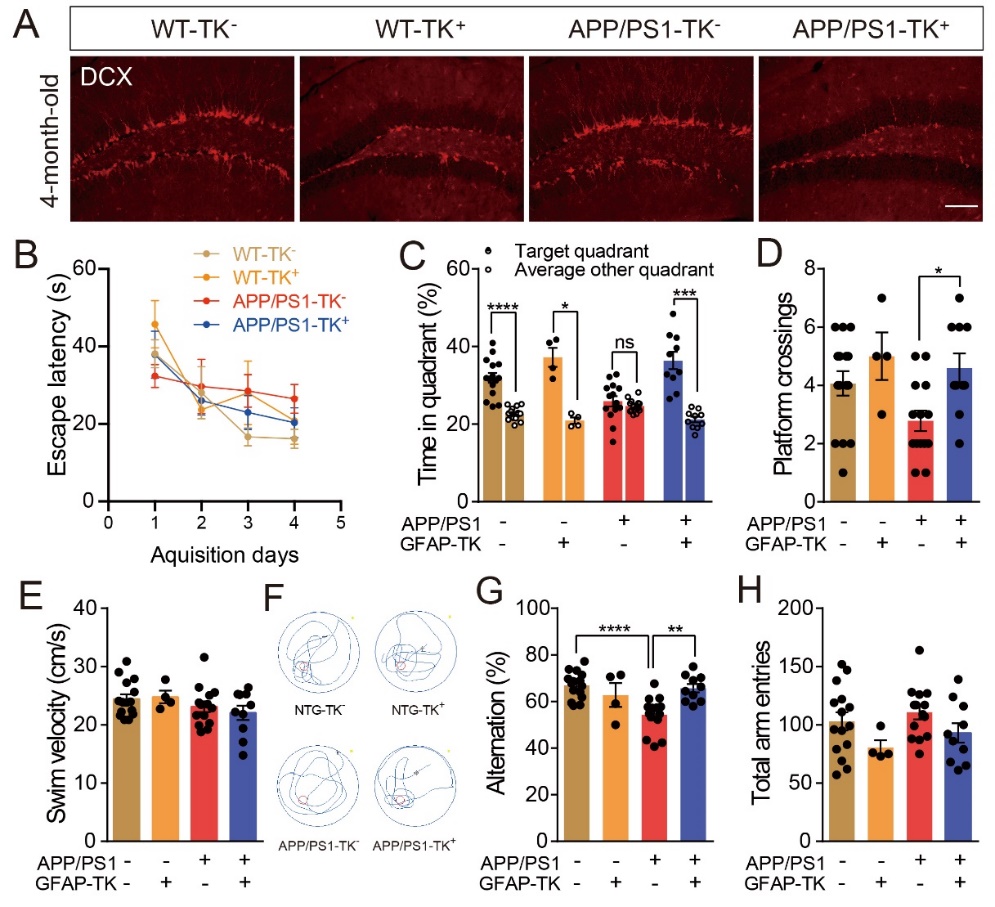
Inhibiting adult neurogenesis improves cognitive functions in AD mice.A, GFAP-TK mice with GCV treatment efficiently inhibits the generation of new neurons (DCX+) in the hippocampus of both WT and AD mice. B-F, Morris water maze test shows that inhibiting adult neurogenesis improves cognitive functions in AD mice. G and H, Y maze test indicates that spatial memory is improved in AD mice after ablating adult neural stem cells.





 Location :
Location : 

